- 5 months ago
What Does a White Reflex in a Baby’s Eye Mean?
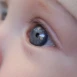
What Is Leukocoria (White Eye Reflex)?
Leukocoria is the presence of a white or grayish reflection from the pupil, which is normally black. In healthy eyes, the flash of a camera typically produces a red reflex due to the retina’s blood supply. A white glow can be a sign that something is blocking light reflection from the retina.
Possible Causes of White Reflex in Infants
1. Retinoblastoma (Eye Tumor)
- The most common malignant eye tumor in children
- Usually occurs before age 5
- White reflex, misalignment (strabismus), and vision loss are common signs
- Early detection can save both vision and life
2. Congenital Cataract
- Clouding of the eye lens present at birth
- May be due to genetic disorders, infections, or metabolic issues
- Often associated with strabismus and vision impairment
3. Persistent Fetal Vasculature (PFV)
- Failure of embryonic blood vessels in the eye to regress
- Usually affects one eye
- May cause a small, opaque white spot and impaired vision
4. Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
- Affects premature babies with abnormal retinal vessel development
- Can lead to leukocoria in advanced stages
- Requires laser treatment in some cases
5. Coats Disease
- Abnormal blood vessel growth in the retina
- Typically affects one eye
- Leads to fluid leakage and white reflex over time
6. Intraocular Infections (e.g., Toxoplasmosis, CMV)
- Infections during pregnancy can damage the baby’s retina
- May cause scarring and white appearance in the eye
- Often accompanied by vision impairment
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- White reflex seen in flash photography (especially in one eye)
- White, gray, or dull pupil when looking directly
- Eye misalignment (strabismus) or constant eye movement
- Baby avoids eye contact or doesn’t track objects
These signs may indicate underlying eye conditions requiring urgent evaluation by a pediatric ophthalmologist.
How Is It Diagnosed?
- Fundus (retinal) examination with ophthalmoscopy
- Ocular ultrasound for intraocular masses
- MRI or CT if structural abnormalities or tumors are suspected
- Biopsy in rare cases (for retinoblastoma confirmation)
Treatment Options Based on Diagnosis
|
Condition |
Treatment Approach |
|
Retinoblastoma |
Chemotherapy, laser therapy, cryotherapy, or eye removal (enucleation) |
|
Cataract |
Surgical removal of the lens, artificial lens implantation |
|
PFV / ROP |
Laser surgery or vitrectomy |
|
Infections |
Antiviral or antibiotic medications, steroids as needed |
Parental Guidance and Monitoring Tips
- Review your baby’s flash photographs for eye reflex
- Monitor for eye contact and object tracking
- Ensure both eyes appear symmetrical and equally sized
- Seek prompt care for any signs of squinting or eye drift
Early detection of leukocoria can prevent vision loss and even save lives in the case of tumors like retinoblastoma.